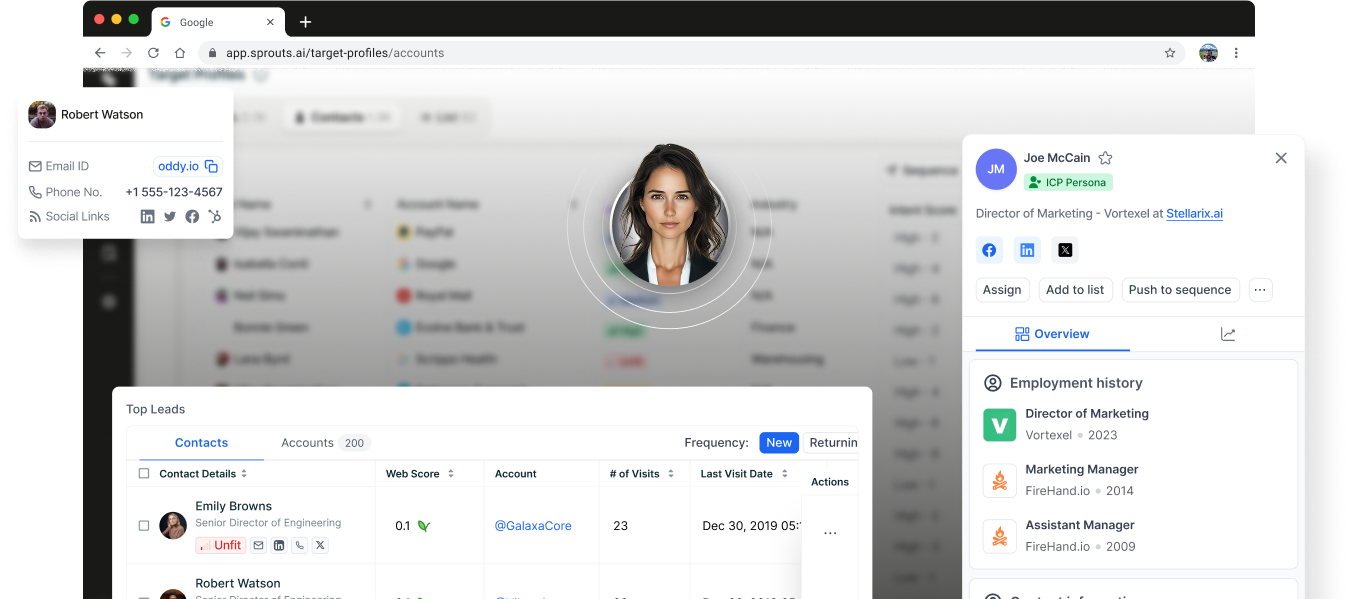
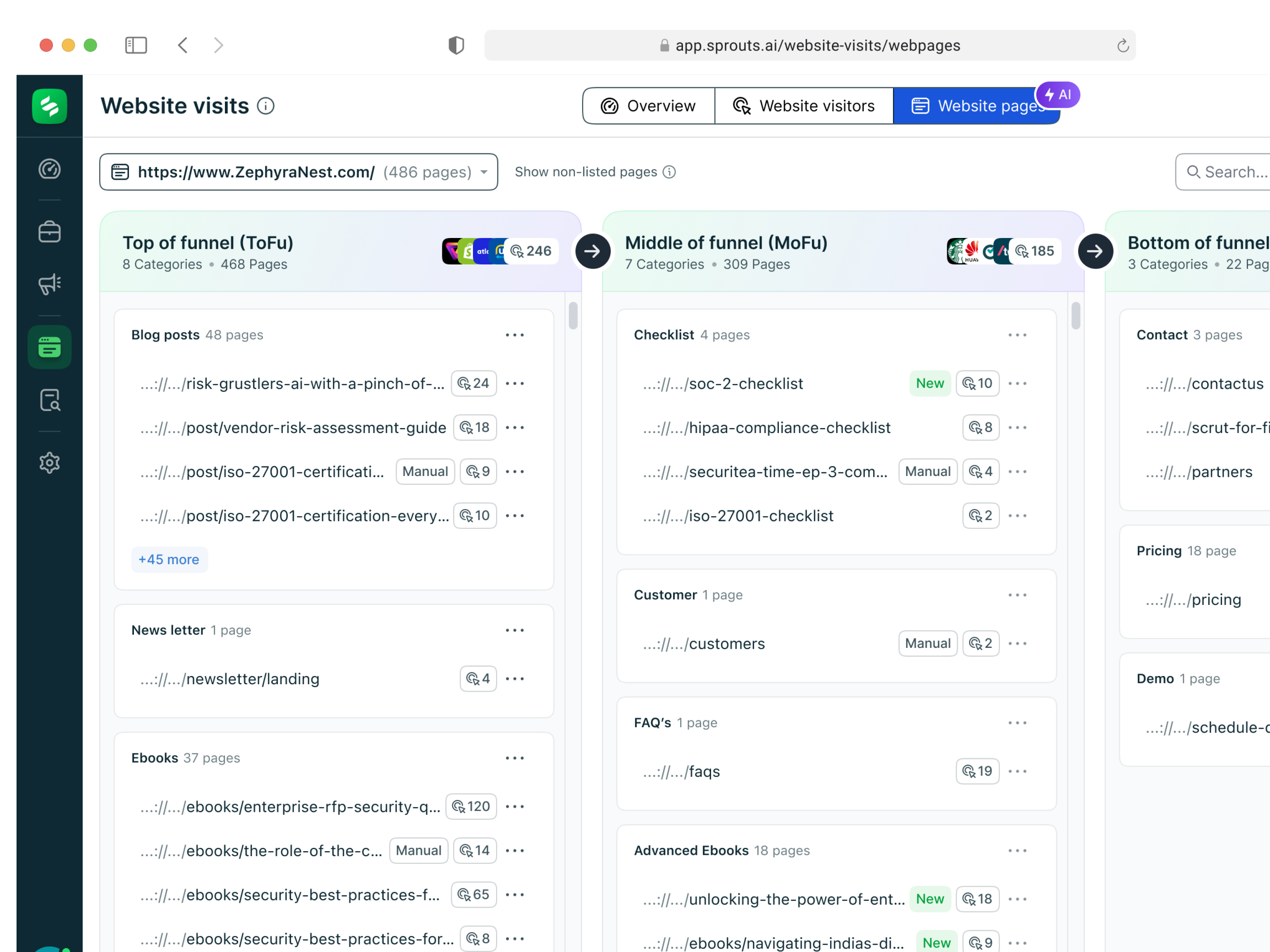
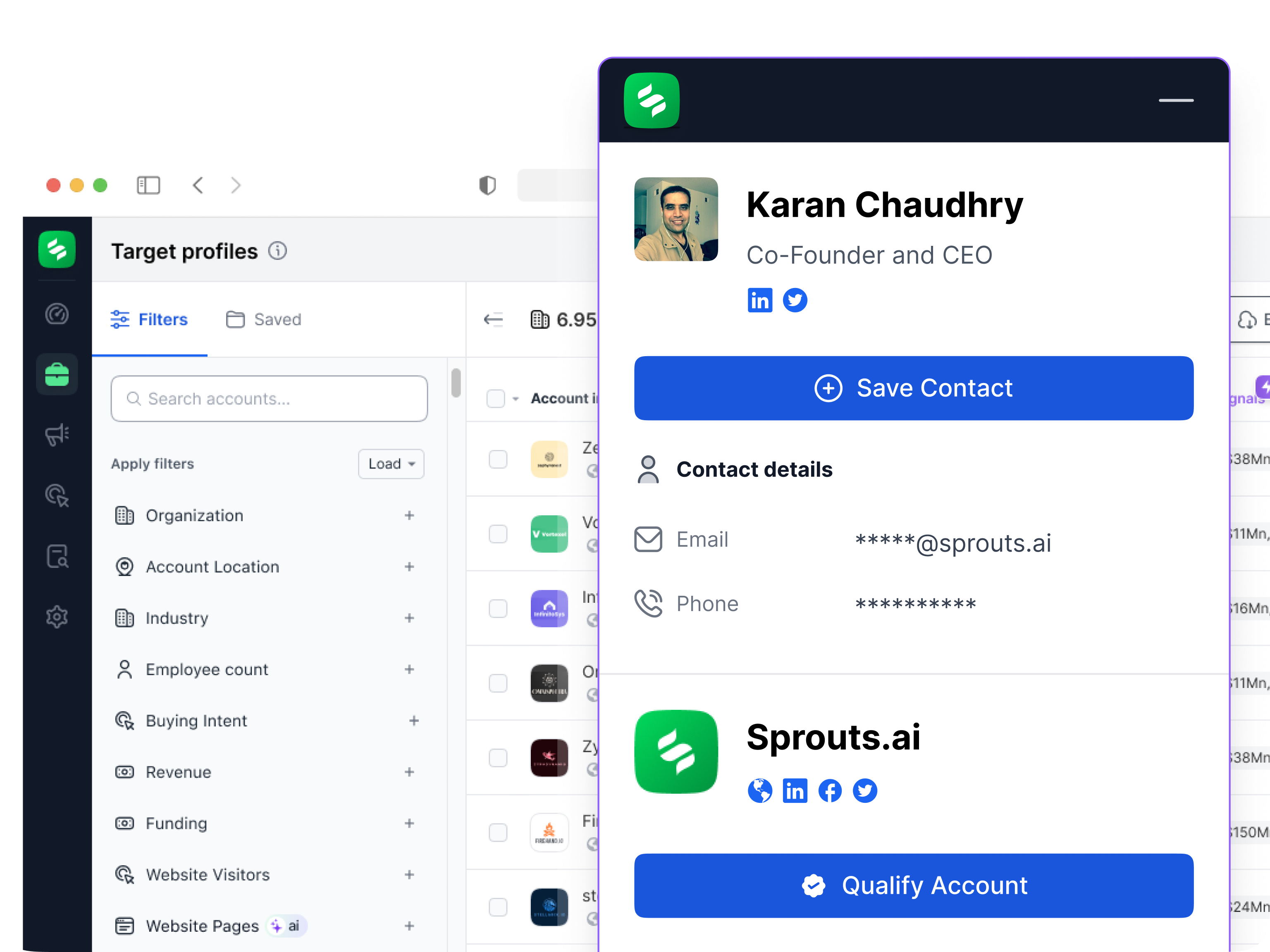
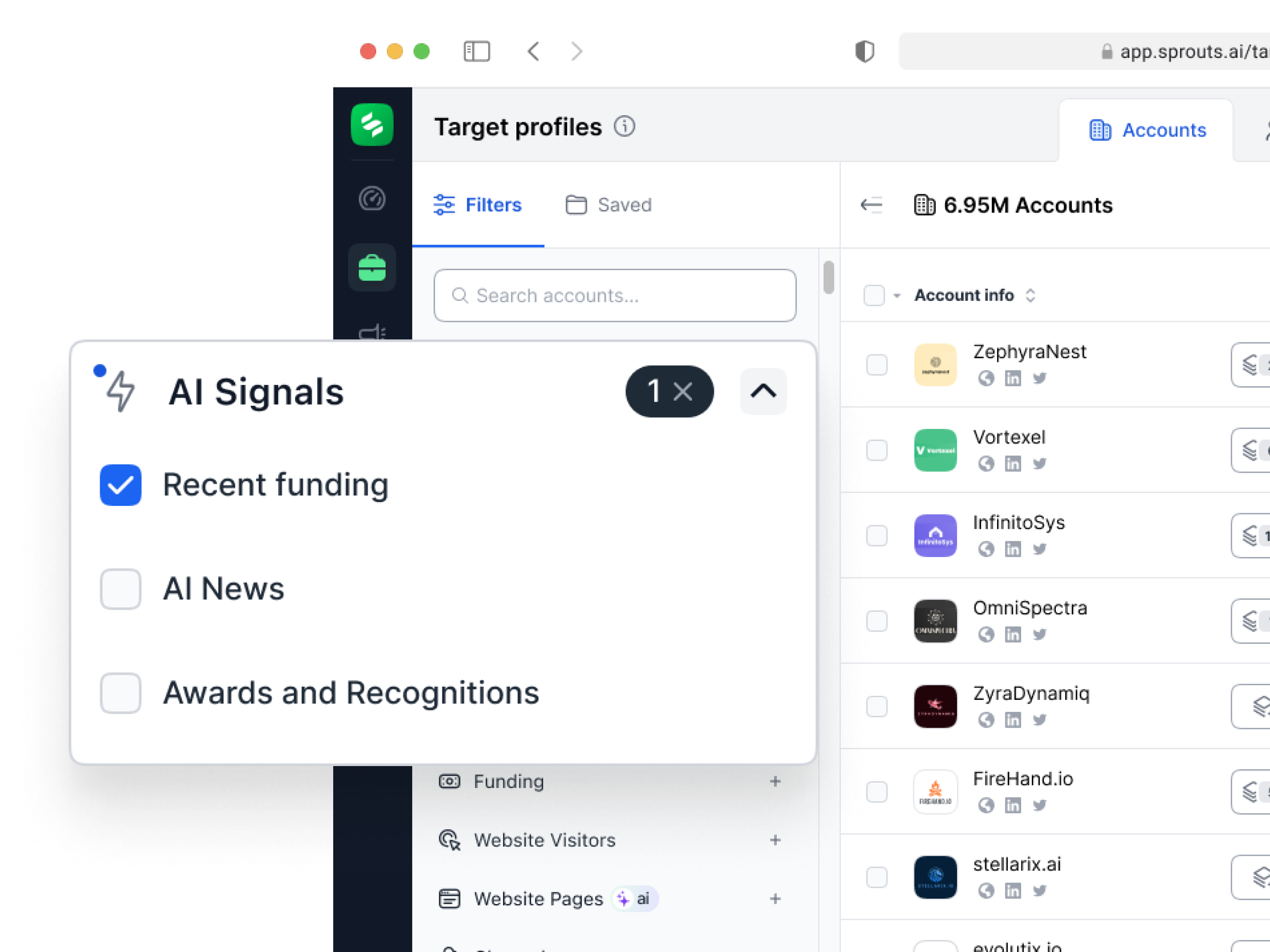
Building Stronger Client Relationships in Real Estate with Targeted Marketing
In real estate, establishing and maintaining strong relationships with clients is crucial for long-term success. With clients seeking personalized experiences and tailored services, it is no longer enough to just offer a property. Real estate professionals need to engage in strategies that build tru...